141. Linked List Cycle
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output: true
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the second node.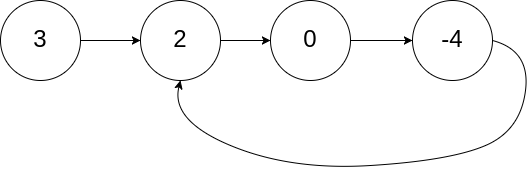

Last updated
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output: true
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the second node.


Last updated
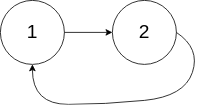
Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
Output: true
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the first node.Input: head = [1], pos = -1
Output: false
Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.// Slow and Fast Pointers
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) { // time: O(n); space: O(1)
if (!head || !head->next) return false;
ListNode *slow = head, *fast = head;
while (fast && fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast) return true;
}
return false;
}